# 数组
# 一、简介
# 优点
- 定义简单
- 按照索引访问元素速度快
# 缺点
- 数组只能存储一种类型的数据
- 数组大小一旦确定后不能更改
- 根据内容查找元素速度慢
- 数组的空间必须是连续的
- 增加、删除元素效率慢
重点目标:
- 掌握数组方法
- 实现一个支持动态扩容的数组
- 实现一个大小固定的有序数组,支持动态增删改操作
- 实现两个有序数组合并为一个有序数组
# 二、使用
# 1. 创建与读写
# 字面量
var num = [1, 5, 6, 10];
# 构造函数
var num = new Array(1, 5, 6, 10);
判断是否为数组? Array. isArray()
# 2. 存取函数
一组用来访问数组元素的函数,叫存取函数
# indexOf()
该函数返回指定查找的值在目标值中是否存在,如果存在,返回该值在数组中的索引,不存在则返回 -1
let word = ["A", "B", "C", "D"];
let result = word.indexOf("A");
console.log(result); // 0
let test = word.indexOf("F");
console.log(test); // -1
2
3
4
5
# join() 和toString()
将数组转化为字符串,但join可以自定义拼接的中间符号,默认逗号。
let arr = ["A", "B", "C"]
console.log(arr.join()) // A,B,C
console.log(arr.toString()) // A,B,C
console.log(arr.join('-')) // A-B-C
2
3
4
# concat()
通过合并多个数组来形成新数组,不去重
let arr1 = ["A", "B", "C"]
let arr2 = ["C", "D"]
let arr = arr1.concat(arr2)
console.log(arr) // ["A", "B", "C", "C", "D"]
2
3
4
# splice()
截取一个数组的子集作为一个新数组,原数组会发生改变
let arr1 = ["A", "B", "C", "D"]
let arr = arr1.splice(1, 2, 'E') // 索引为1的位置开始删除2个数,并在索引1处加入E
console.log(arr) // arr为删除的索引为1的B和索引为2的C
console.log(arr1) // arr1为截取新增后的数组
2
3
4
# 3. 可变函数
不去引用数组中的某个元素,就能改变数组内容,这种函数称它为可变函数。
# push()和unshift(),pop()和shift()
- push():在数组末尾添加元素
- unshift():在数组开头添加元素
- pop():在数组末尾删除元素
- shift():在数组末尾删除元素
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
arr.push(5)
console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
arr.unshift(0)
console.log(arr) // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
arr.pop()
console.log(arr) // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
arr.shift()
console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3, 4]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# splice()、sort()、reverse()
- splice():对数组可删除可添加元素
- sort():排序数组。针对字母的字符串类型排序准确,当数字或者数字的字符串需要使用一个函数来处理。a-b为升序,b-a为倒序。利用了两数相减,如果结果为正,那么被减数大于减数,如果结果为 0,则两数相等,而如果结果为负,说明被减数小于减数
- reverse():翻转数组
// sort
let arr = [3, 41, 5]
let strArr = ['3', '41', '5']
let str = ['a', 'c', 'b']
arr.sort()
strArr.sort()
str.sort()
console.log(arr) // [3, 41, 5]
console.log(strArr) // [3, 41, 5]
console.log(str) // ["a", "b", "c"]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// sort
let arr = [3, 4, 1, 2, 5]
arr.sort((a, b) => a - b)
console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
2
3
4
//reverse
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(arr.reverse()) // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
2
3
# 4. 迭代器方法
迭代函数通过对数组中的元素逐个应用,来操作返回相应的值
| 是否返回新数组 | 方法 |
|---|---|
| 不返回 | forEach() 、every()、some()、reduce() |
| 返回 | map() 和 filter() |
# forEach()
array. forEach(function(currentValue, index, arr), thisValue)
调用数组的每个元素,并将元素传递给回调函数
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
let squareArr = []
arr.forEach(item => {
squareArr.push(item * item)
})
console.log(squareArr) // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
2
3
4
5
6
# every()
every() 返回值为布尔类型,对于应用的所有元素该函数都返回 true,则该方法返回 true
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
let show = arr.every(item => {
return item < 5
})
console.log('arr的每个数据' + (show ? '都' : '不都') + '小于5') //arr的每个数据不都小于5
2
3
4
5
# some()
some()返回值为布尔类型,只要一个元素使得函数返回true,该方法就返回true
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
let show = arr.some(item => {
return item < 5
})
console.log('arr的数据' + (show ? '存在' : '不存在') + '小于5的元素') //arr的数据存在小于5的元素
2
3
4
5
# reduce()
接收一个函数作为累加器,数组中的每个值(从左到右)开始缩减,最终计算为一个值 reduce功能一可以对元素进行求和,功能二将数组元素连接成字符串。数字求和,字符串拼接
let arr1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
let arr2 = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5']
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
console.log(arr1.reduce(add)) // 15
console.log(arr2.reduce(add)) // 12345
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# map()
调用数组的每个元素,并将元素传递给回调函数
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
let squareArr = arr.map(item => {
return item * item
})
console.log(squareArr) // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
2
3
4
5
# filter()
filter 和 every 相似,区别在于当所有的元素使改函数为 true 时,它并不返回布尔类型,而是返回一个新数组
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
let show = arr.filter(item => {
return item < 5
})
console.log(show) //[1, 2, 3, 4]
2
3
4
5
# 三、代码题
# 1. 数组中重复的数(#442)
给定一个整数数组 a, 其中1≤ a[i]≤ n( n为数组长度), 其中有些元素出现两次而其他元素出现一次。
找到所有出现两次的元素。
你可以不用到任何额外空间并在O(n) 时间复杂度内解决这个问题吗?
示例:
输入: [4, 3, 2, 7, 8, 2, 3, 1]
输出: [2, 3]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
解法一: 常规解法,先排序,如果数字重复应该处在相邻位置,但不符合复杂度为O(n)
var findDuplicates = function(nums) {
let len = nums.length
let arr = []
if (len < 2) return arr
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b)
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
arr.push(nums[i])
}
}
return arr
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
解法二: 遍历数组,下标为abs(nums[i]) -1的值取反(-1是为了防止访问数组越界:a[i] ≤ n), 如果遍历到的下标为abs(nums[i]) -1的值为负,说明abs(nums[i])出现了两次
var findDuplicates = function(nums) {
let result = []
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[Math.abs(nums[i]) - 1] > 0)
nums[Math.abs(nums[i]) - 1] *= -1
else
result.push(Math.abs(nums[i]))
}
return result
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
电话号码组合(公式运算) 卡牌分组(归类运算) 种花问题(筛选运算) 格雷编码(二进制运算)
https://www.cnblogs.com/yalong/p/11606865.html https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42671045/article/details/89842848
# 链表
- 链表不需要一块连续的内存空间,它通过“指针”将一组零散的内存块串联起来使用。
- 动态数据结构,不需要处理固定容量的问题。
- 丧失随机访问的能力
重点目标:
- 实现单链表、循环链表、双向链表,支持增删操作
- 实现单链表反转
- 实现两个有序的链表合并为一个有序链表
- 实现求链表的中间结点
- 链表如何排序
- 检测链表闭环
# 一、单链表
# 1. 简介
# 特点
- 头结点记录链表基地址,通过遍历可得到整条链表
- 尾结点指向一个空地址null

# 链表的删除与插入
**
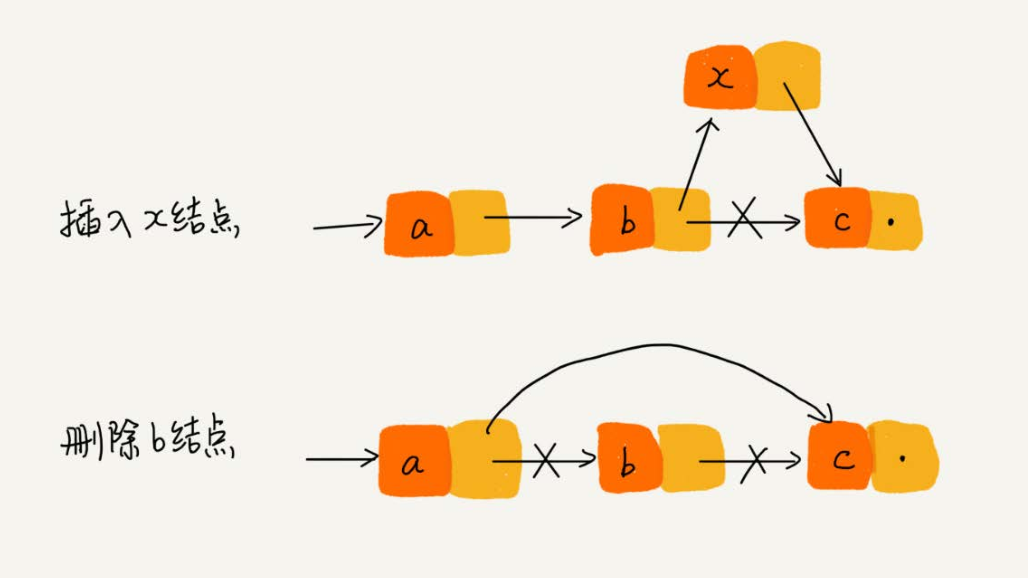
# 2. 手写
# 基础链表
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.next = null
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = new Node('head')
}
/**
* 根据数值value找节点元素element。空链表返回null
* @param {*} value
*/
findByValue(value) {
let currentNode = this.head.next
while (currentNode !== null && currentNode.value !== value) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return currentNode
}
/**
* 根据数值index找节点元素element。
* 空链表返回null
*/
findByIndex(index) {
let currentNode = this.head.next
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
if (currentNode === null) return currentNode
else {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
}
return currentNode
}
/**
* 末尾添加元素
*/
append(item) {
let currentNode = new Node(item)
let prevNode = this.head
while (prevNode.next) {
prevNode = prevNode.next
}
prevNode.next = currentNode
}
/**
* 指定元素后插入元素
* 首先找出指定元素,新建新元素
* 然后将新元素指向指定元素原先的next,指定元素的next指向新元素
*/
insert(item, newItem) {
let prevNode = this.findByValue(item)
let currentNode = new Node(newItem)
if (!currentNode) return
currentNode.next = prevNode.next
prevNode.next = currentNode
}
/**
* 查找前一个元素
*/
findPrev(value) {
let currentNode = this.head
while (currentNode.next !== null && currentNode.next.value !== value) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return currentNode
}
/**
* 删除元素
*/
remove(item) {
let prevNode = this.findPrev(item)
if (!prevNode) return
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next
}
/**
* 编辑元素
*/
edit(item, newItem) {
let currentNode = this.findByValue(item)
currentNode.value = newItem
}
/**
* 遍历出所有数据
*/
display() {
let currentNode = this.head.next
while (currentNode !== null) {
console.log(currentNode.value)
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
}
}
const LList = new LinkedList()
LList.append('1')
LList.append('2')
LList.append('3')
LList.append('4')
LList.display()
console.log('--------------------')
console.log(LList.findByValue('2'))
console.log('--------------------')
console.log(LList.findPrev('2'))
console.log('--------------------')
console.log(LList.findByIndex(2))
console.log('--------------------')
LList.insert('4', '5')
LList.display()
console.log('--------------------')
LList.edit('5', '6')
LList.display()
console.log('--------------------')
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
# 记录长度的链表
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element
this.next = null
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = new Node(null)
this.size = 0
}
/* 根据索引查找找元素
* 当索引不在0=size间时返回null
循环索引拿到当前节点
*/
findByIndex(index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) return null
let current = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next
}
return current
}
/* 根据数据查找找元素
* 如果当前链表是空链表返回null
循环链表,当节点数据等于查找的element返回该节点
*/
findByValue(element) {
let current = this.head
if (current.next === null) return null
while (current.element !== element) {
current = current.next
}
return current
}
/* 根据value找元素“index”
* 默认当前节点为头结点,循环链表,当节点的数值等于查找的value时返回索引,否则返回-1
*/
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head
for (let i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
if (current.element === element) return i
current = current.next
}
return -1
}
/* 向链表追加节点
* 如果链表为空时,头节点也是尾结点,将头指针next指向新的节点,新节点的next不需要定义则为null;如果链表不为空,则找到最后一个元素,改变该元素的next指向,指到新节点,整个链表长度加一
*/
append(element) {
const node = new Node(element)
if (this.head == null) this.head = node
else {
let current = this.findByIndex(this.size - 1)
current.next = node
}
this.size++
}
// 在链表制定位置插入
insert(pos, element) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.size) return false
let node = new Node(element)
if (pos === 0) {
node.next = this.head
this.head = node
} else {
let prevNode = this.findByIndex(pos - 1)
node.next = prevNode.next
prevNode.next = node
}
this.size++
return true
}
removeAt(pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.size) return null
let current = this.head
if (pos === 0) this.head = current.next
else {
let prevNode = this.findByIndex(pos - 1)
prevNode.next = current.next
}
this.size--
}
remove(element) {
let index = this.indexOf(element)
return this.removeAt(index)
}
// 是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0
}
// 返回链表长度
getSize() {
return this.size
}
// 返回头元素
getHead() {
return this.head
}
// 清空链表
clear() {
this.head = null
this.size = 0
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
# 数组转链表
// 声明链表节点
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.val = value
this.next = null
}
}
// 声明链表的数据结构,原生js没有链表,必须自己造
class NodeList { // 类实例的对象就是head
constructor(arr) {
let head = new Node(arr.shift()) // 声明头部节点,头指针是node节点
let next = head // 当前节点的next指针
arr.forEach(item => {
next.next = new Node(item)
next = next.next
})
return head
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 二、双向链表
(待续)
# 三、循环链表
(待续)
# 四、代码题
# 1. 反转链表(#206)
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1 - > 2 - > 3 - > 4 - > 5 - > NULL
输出: 5 - > 4 - > 3 - > 2 - > 1 - > NULL
进阶:
你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。 你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
解法一: **
- 借用一个null指针代表尾节点指向,默认当前节点为head。不断循环,让当前节点的next指针指向前一个节点。让前一个节点等于当前节点,当前节点等于下一个节点,一直循环到最后,整个链表就被翻转过来了
- 输出尾节点就能将整个链表输出
var reverseList = function(head) {
let [prev, current] = [null, head]
while (current) {
const temp = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = temp
}
return prev
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
68 ms 35. 4 MB
解法二: ** 在解法一的基础上采用递归的方法
var reverseList = function(head) {
return reverse(null, head)
};
function reverse(prev, current) {
if (!current) return prev
let temp = current.next
current.next = prev
return reverse(current, temp)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
60 ms 35. 8 MB
# 2. 环形链表(#141)


解法一: 双指针解法,设置 一个快指针和一个慢指针,当快指针和慢指针相等或者快指针跑到慢指针后面的时候说明有环
- 空链表或者1个元素的链表肯定不能形成环形
- 终止条件fast为尾结点或者倒数尾结点
var hasCycle = function(head) {
if (head === null || head.next === null) return false
let slow = head
let fast = head.next
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast === null || fast.next === null) return false
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
}
return true
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
80 ms 37. 3 MB
解法二: 设置不可能的数据,骗过验证。类似数组的查找重复的数值的解法
var hasCycle = function(head) {
while (head) {
if (head.val == '234jsdf.&342') {
return true
} else {
head.val = '234jsdf.&342'
head = head.next
}
}
return false
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
72 ms 37. 7 MB
解法三: 利用JSON. stringify()不能字符串化含有循环引用的结构
var hasCycle = function(head) {
try {
JSON.stringify(head)
return false
} catch {
return true
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
124 ms 40. 4 MB
# 3. 两两交换链表节点(#24)
给定一个链表, 两两交换其中相邻的节点, 并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值, 而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例:
给定 1 - > 2 - > 3 - > 4, 你应该返回 2 - > 1 - > 4 - > 3.
2
3
4
5
6
7
(待续)
# 4. 链表中间节点(#876)
给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表, 返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点, 则返回第二个中间结点。
示例 1:
输入:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
输出: 此列表中的结点 3(序列化形式:[3, 4, 5])
返回的结点值为 3。(测评系统对该结点序列化表述是[3, 4, 5])。
注意, 我们返回了一个 ListNode 类型的对象 ans, 这样:
ans.val = 3, ans.next.val = 4, ans.next.next.val = 5, 以及 ans.next.next.next = NULL.
示例 2:
输入:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
输出: 此列表中的结点 4(序列化形式:[4, 5, 6])
由于该列表有两个中间结点, 值分别为 3 和 4, 我们返回第二个结点。
提示:
给定链表的结点数介于 1 和 100 之间。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
解法一: ** 利用双指针法,快指针是慢指针两倍跑。当快指针是尾指针或者指向null的时候,慢指针刚刚好在中间
var middleNode = function(head) {
let slow = head
let fast = head
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
}
return slow
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
60 ms 34 MB
#
#
# 5. 删除链表中倒数第N个节点(#19)
给定一个链表, 删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点, 并且返回链表的头结点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1 - > 2 - > 3 - > 4 - > 5, 和 n = 2.
当删除了倒数第二个节点后, 链表变为 1 - > 2 - > 3 - > 5.
说明:
给定的 n 保证是有效的。
进阶:
你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
解法: 利用哨兵节点,查到倒数第n-1个节点的时候改变指向
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
let dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
let length = 0;
let currentNode = head;
while (currentNode) {
length++;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
length -= n;
currentNode = dummy;
while (length) {
length--;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
currentNode.next = currentNode.next.next;
return dummy.next;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
60 ms 34. 5 MB
#
# 6. 删除链表中的节点(#237)

解法: 让最后一个节点拿到倒数第二个节点的值和指向
var deleteNode = function(node) {
node.val = node.next.val
node.next = node.next.next
};
2
3
4
72 ms 36. 2 MB
#
# 7. 合并两个有序链表(#21)
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。 新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入: 1 - > 2 - > 4, 1 - > 3 - > 4
输出: 1 - > 1 - > 2 - > 3 - > 4 - > 4
2
3
4
5
6
解法: 递归法:将两个链表的值进行对比,最小的值的指针指向之后第二小的数值
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
if (l1 === null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 === null) {
return l1;
}
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
72 ms 35. 9 MB
# 综合与拓展
# 1. 概览
(思维导图待续)
# 2. 数组的删除与插入为什么是低效的?
插入: 假设数组的长度为 n ,如果我们需要将一个数据插入到数组中的第 k 个位置。为了把第 k 个位置腾出来,给新来的数据,我们需要将第 k ~ n 这部分的元素都顺序地往后挪一位。
- 插入末尾,时间复杂度为O(1)
- 插入开头,时间复杂度为O(n)
- 平均时间复杂度为O(n)
为了避免搬移可以直接将第 k 位的数据搬移到数组元素的最后,把新的元素直接放入第 k 个位置(快排思想)
删除: 和插入一样需要搬移 多次删除时,为了避免数据会被搬移多次,我们可以先记录下已经删除的数据。每次的删除操作并不是真正地搬移数据,只是记录数据已经被删除。当数组没有更多空间存储数据时,我们再触发执行一次真正的删除操作,这样就大大减少了删除操作导致的数据搬移
JVM标记清除垃圾回收算法
# 3. 数组的访问越界问题?
假如数组有n个元素,当我们访问除了n个元素之外的元素时,则出现访问越界
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ int i = 0; int arr[3] = {0}; for(; i<=3; i++){ arr[i] = 0; printf("hello world\n"); } return 0; } 你发现问题了吗?这段代码的运行结果并非是打印三行 “hello word” ,而是会无限打印 “hello world” ,这是为什么呢? 因为,数组大小为 3 , a[0] , a[1] , a[2] ,而我们的代码因为书写错误,导致 for 循环的结束条件错写为了 i<=3 而非 i<3 ,所以当 i=3 时,数组 a[3] 访问越界。 我们知道,在 C 语言中,只要不是访问受限的内存,所有的内存空间都是可以自由访问的。根据我们前面讲的数组寻址公式, a[3] 也会被定位到某块不属于数组的 内存地址上,而这个地址正好是存储变量 i 的内存地址,那么 a[3]=0 就相当于 i=0 ,所以就会导致代码无限循环
编译器分配内存和字节对齐有关 数组 3 个元素 加上一个变量 a 。 4 个整数刚好能满足 8 字节对齐 所以 i 的地址恰好跟着 a2 后面 导致死循 环。。如果数组本身有 4 个元素 则这里不会出现死循环。。因为编译器 64 位操作系统下 默认会进行 8 字节对齐 变量 i 的地址就不紧跟着数组后面了
# 4. 为什么大多数语言,数组编号从0而不是1开始?
- 减少cpu的运算量
在数组存储的内存模型看,a代表数组的首地址,a[0]为偏移为0的位置,a[k]代表偏移k个type_size(int 类型数据,所以 type_size 就为 4 个字节)的位置 0: a[k]=base + k*type_size 1: a[k]=base + (k-1)*type_size 从1开始编号则每次随机访问多出一次减法运算。
- C语言设计者使用0,其他语言沿用。
但如Matlab不是cong0计数或者python支持负数下标
# 5. 二维数组的内存寻址公式?
对于 m * n 的数组, a [ i ][ j ] (i < m, j < n) 的地址为:
a[i][j] = base + (i * n + j) * type_size
# 6. 链表适合插入、删除,时间复杂度为O(1), 数组适合查找,查找时间复杂度为)(1)?
数组适合查找操作。但是时间复杂度不为O(1)。数组支持随机访问,根据下标随机访问的时间复杂度才是O(1)
已排序数组,二分查找,时间复杂度O(logn)
